 |
| Space Launch |
SATELLITES and other spacecrafts must be accelerated to a very high speed to go into orbit around the Earth. Space vehicles can conserve energy by launching in the same direction as the rotation of the Earth.The Earth makes one rotation a day and this rotation is from west to east (this is why the Sun appears to move from east to west). If effective use is made of the Earth's rotation to conserve energy, a greater load can be lifted than if the rocket was launched in the other direction.
Getting something into space is easy. You just have to get it 100 km (62 mi) up. Amateur rocketeers have accomplished this. If that’s all you are trying to do, just point the rocket straight up.
If you want to put a payload into orbit, that’s much more difficult and involves accelerating the payload so that it moves around the earth fast enough to not fall into the earth. At the height of the ISS (~400km) that’s about 8km/s. At the equator, the earth revolves at about 465m/s. In orbital mechanics we talk about dV or delta V. Thus an anterograde (with the earth’s spin) orbit has a dV of ~7.5 km/s and a retrograde (opposite the earth’s spin) orbit has a dV of ~8.5 km/s. You can see that there is a significant advantage to launching West to East.
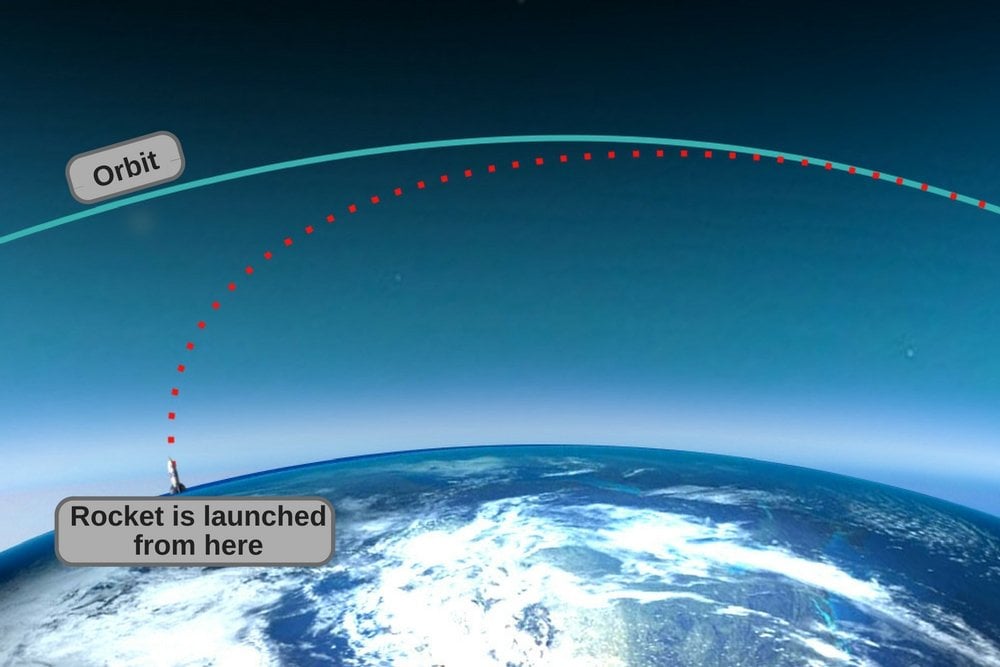
Interestingly, there is an additional consideration. All rockets (except now SpaceX’s) fall back to earth after launch. Thus, mission planners must consider where the spent boosters will land. Every nation that has orbital launch capabilities has put their launch facilities in a location where they can launch towards the East and their spent boosters will fall in an uninhabited area, except one. Israel doesn’t have any way to launch rockets to the East and not provoke another war. So instead, Israel launches to the West over the med, making Israel the only spacefaring country that launches everything into a retrograde orbit.
However, not all satellites are launched due east. For example, Earth observation satellites must be able to monitor the whole of the Earth's surface so their orbits pass over the poles (polar orbit), and they are launched to the south.
So, by reading this sort of information about space launching, now you might have acquaintanced the basicc knowledge about this field of era. And you might also be aware about the Moon mission of India which was Chandrayan II was recently launched. So can you tell, in which direction was the launching of the Chandrayan II headed ?



0 Comments